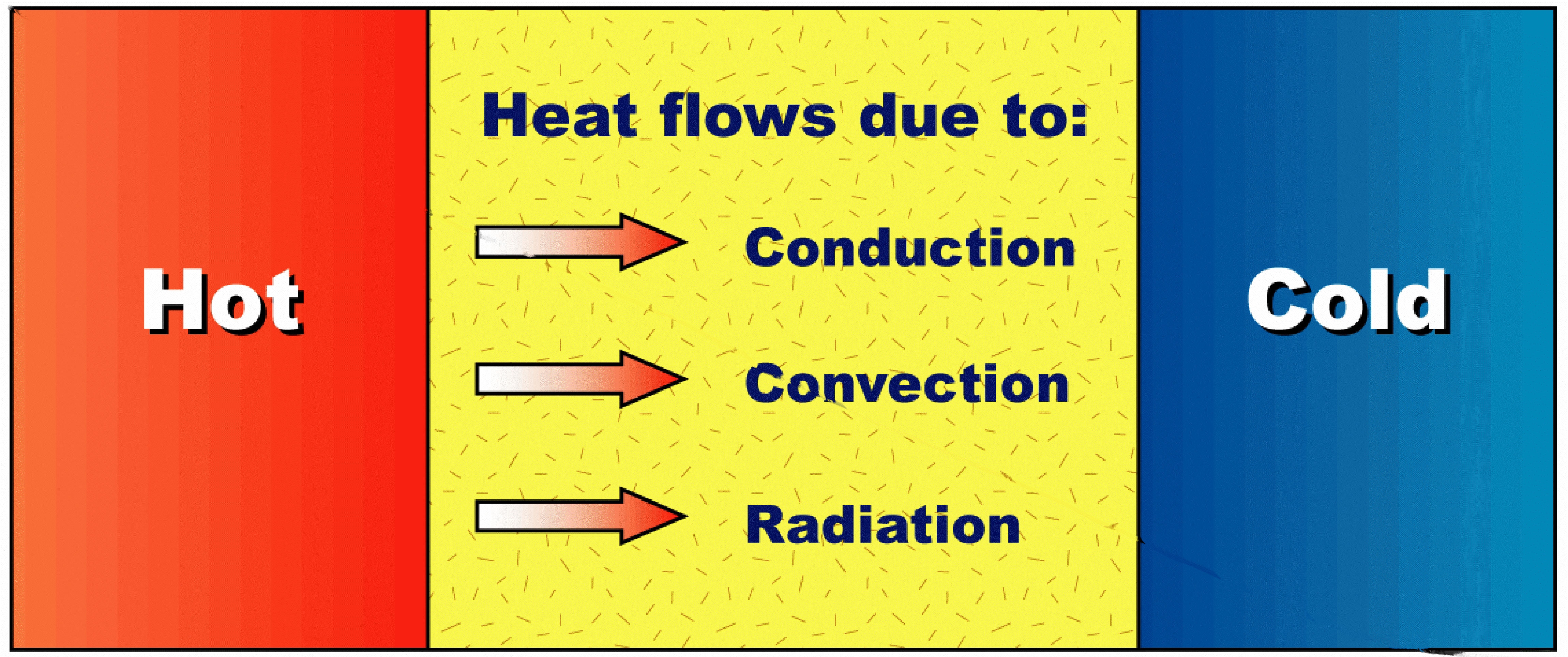
Conductors and Insulators
Conductors are made of materials that electricity can flow through easily.
These materials are made up of atoms whose electrons can move away freely.
Some examples of conductors are:
- Copper
- Aluminum
- Platinum
- Gold
- Silver
- Water
- People and Animals
- Trees
Insulators are materials opposite of conductors. The atoms are not easily freed and are stable, preventing or blocking the flow of electricity.
Some examples of insulators are:
- Glass
- Porcelain
- Plastic
- Rubber
Electricity will always take the shortest path to the ground. Your body is 60% water and that makes you a good conductor of electricity. If a power line has fallen on a tree and you touch the tree you become the path or conductor to the ground and could get electrocuted.
The rubber or plastic on an electrical cord provides an insulator for the wires. By covering the wires, the electricity cannot go through the rubber and is forced to follow the path on the aluminum or copper wires.
Electrical Conductors
Electrical conductors allow electric current to flow easily because of the make up of their atoms. In a conductor, the outer electrons of the atom are loosely bound and can freely move through the material when an electric charge is applied.
Conductive Materials
In general, the best electrical conductors are metals. Metals tend to have electrons in the outer layer of their atoms that are freely shared. The most conductive of all the elements is silver. Unfortunately, silver is too rare and expensive to use in most electrical equipment. Today, the most commonly used electrical conductor is copper. Copper is used in electrical wiring and electrical circuits throughout the world.
Conductance and Resistance
Another way to think of conductance is as the opposite of resistance. The resistance of a material is a measurement of how well a material opposes the flow of electric current. Sometimes conductance is represented by the letter “G” where G is the inverse of resistance, R.
Using Ohm’s law we know that resistance is equal to voltage divided by current or R = V/I, therefore
Superconductors
A superconductor is a material that is a perfect conductor. It has an electrical resistance of zero. All of the superconductors that have been discovered by scientists to date require a very cold temperature on the order of minus 234 degrees C in order to become superconductors.
Electrical Insulators
The opposite of a conductor is an insulator. An insulator opposes the flow of electricity. Insulators are important to keep us safe from electricity. The wire that carries electricity to your computer or television is covered with a rubber-like insulator that protects you from getting electrocuted. Good insulators include glass, the air, and paper.
Semiconductors
Some materials behave in between a conductor and an insulator. These materials are called semiconductors. Semiconductors are important in electronics such as computers and mobile phones because their conductivity can be controlled allowing for current to flow in just one direction or only under certain circumstances. The most commonly used semiconductor in electronics today is silicon.
Interesting Facts about Electrical Conductors and Insulators
- Most good electrical conductors are also good conductors of heat.
- Temperature can play an important role in the conductance of a material. In general, the higher the temperature the lower the conductivity as resistance increases with temperature.
- Aluminum has a lower conductivity than copper, but is sometimes used in wiring for lower cost.
- Many electronics companies are headquartered in “Silicon Valley”, California, which is nicknamed after the semiconductor silicon.
Join these Online Classes today from comfort of your couch or bed. Get help in Homework, Projects, Assignments, Exam Preparation. Radix Tree Online Education Transforming System Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, English Language, English Literature Classes.
Book your Trial Lesson for free today. Just click the following link below: