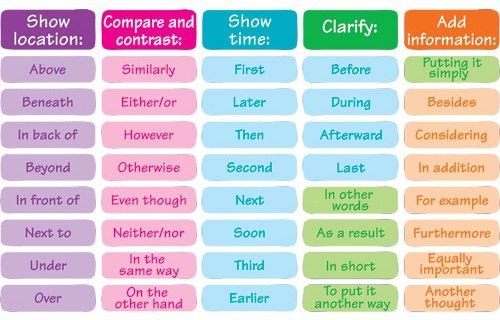
Linking Words and Phrases
You can use words or short phrases which help to guide your reader through your writing, and to link sentences, paragraphs and sections both forwards and backwards. Good use will make what you have written easy to follow; bad use might mean your style is disjointed, probably with too many short sentences, and consequently difficult to follow. Your mark could be affected either way.
The best way to “get a feel” for these words is through your reading. Most textbooks and articles are well-written and will probably include a lot of these cohesive devices. Note how they are used and try to emulate what you have read. Do make sure though that you fully understand their meaning: incorrect use could change completely what you’re trying to say. Try to use a variety of expressions, particularly in longer pieces of writing.
Don’t forget “AND”! Two short sentences are often best connected together with this little word.
There follows a list of words and phrases that can be used. The list is not exhaustive, and BE CAREFUL: although grouped together, none is totally synonymous. Their position in the sentence can also vary; this is where your reading and dictionary come in.
Linking words help you to connect ideas and sentences, so that people can follow your ideas.
Giving examples
For example
For instance
Namely
The most common way of giving examples is by usingfor example or for instance.
Namely refers to something by name.
“There are two problems: namely, the expense and the time.”
Adding information
And
In addition
As well as
Also
Too
Furthermore
Moreover
Apart from
In addition to
Besides
Ideas are often linked by and. In a list, you put a comma between each item, but not before and.
“We discussed training, education and the budget.”
Also is used to add an extra idea or emphasis. “We also spoke about marketing.”
You can use also with not only to give emphasis.
“We are concerned not only by the costs, but also by the competition.”
We don’t usually start a sentence with also. If you want to start a sentence with a phrase that means also, you can use In addition, or In addition to this…
As well as can be used at the beginning or the middle of a sentence.
“As well as the costs, we are concerned by the competition.”
“We are interested in costs as well as the competition.”
Too goes either at the end of the sentence, or after the subject and means as well.
“They were concerned too.”
“I, too, was concerned.”
Apart from and besides are often used to mean as well as, or in addition to.
“Apart from Rover, we are the largest sports car manufacturer.”
“Besides Rover, we are the largest sports car manufacturer.”
Moreover and furthermore add extra information to the point you are making.
“Marketing plans give us an idea of the potential market. Moreover, they tell us about the competition.”
Summarizing
In short
In brief
In summary
To summarize
In a nutshell
To conclude
In conclusion
We normally use these words at the beginning of the sentence to give a summary of what we have said or written.
Sequencing ideas
The former, … the latter
Firstly, secondly, finally
The first point is
Lastly
The following
The former and the latter are useful when you want to refer to one of two points.
“Marketing and finance are both covered in the course. The former is studied in the first term and the latter is studied in the final term.”
Firstly, … secondly, … finally (or lastly) are useful ways to list ideas.
It’s rare to use “fourthly”, or “fifthly”. Instead, try the first point, the second point, the third point and so on.
The following is a good way of starting a list.
“The following people have been chosen to go on the training course: N Peters, C Jones and A Owen.”
Giving a reason
Due to / due to the fact that
Owing to / owing to the fact that
Because
Because of
Since
As
Due to and owing to must be followed by a noun.
“Due to the rise in oil prices, the inflation rate rose by 1.25%.”
“Owing to the demand, we are unable to supply all items within 2 weeks.”
If you want to follow these words with a clause (a subject, verb and object), you must follow the words with the fact that.
“Due to the fact that oil prices have risen, the inflation rate has gone up by 1%25.”
“Owing to the fact that the workers have gone on strike, the company has been unable to fulfill all its orders.”
Because / because of
Because of is followed by a noun.
“Because of bad weather, the football match was postponed.”
Because can be used at the beginning or in the middle of a sentence. For example, “Because it was raining, the match was postponed.”
“We believe in incentive schemes, because we want our employees to be more productive.”
Since / as
Since and as mean because.
“Since the company is expanding, we need to hire more staff.”
As the company is expanding, we need to hire more staff.”
Giving a result
Therefore
So
Consequently
This means that
As a result
Therefore, so, consequently and as a result are all used in a similar way.
“The company are expanding. Therefore / So / Consequently / As a result, they are taking on extra staff.”
So is more informal.
Contrasting ideas
But
However
Although / even though
Despite / despite the fact that
In spite of / in spite of the fact that
Nevertheless
Nonetheless
While
Whereas
Unlike
In theory… in practice…
But is more informal than however. It is not normally used at the beginning of a sentence.
“He works hard, but he doesn’t earn much.”
“He works hard. However, he doesn’t earn much.”
Although, despite and in spite of introduce an idea of contrast. With these words, you must have two halves of a sentence.
“Although it was cold, she went out in shorts.”
“In spite of the cold, she went out in shorts.”
Despite and in spite of are used in the same way as due to and owing to. They must be followed by a noun. If you want to follow them with a noun and a verb, you must use the fact that.
“Despite the fact that the company was doing badly, they took on extra employees.”
Nevertheless and nonetheless mean in spite of that or anyway.
“The sea was cold, but he went swimming nevertheless.” (In spite of the fact that it was cold.)
“The company is doing well. Nonetheless, they aren’t going to expand this year.”
While, whereas and unlike are used to show how two things are different from each other.
“While my sister has blue eyes, mine are brown.”
“Taxes have gone up, whereas social security contributions have gone down.”
“Unlike in the UK, the USA has cheap petrol.”
In theory… in practice… show an unexpected result.
“In theory, teachers should prepare for lessons, but in practice, they often don’t have enough time.”
| Listing | Giving examples | Generalising |
| first, second, third | for example | in general |
| first, furthermore, finally | for instance | generally |
| to begin, to conclude | as follows: | on the whole |
| next | that is | as a rule |
| Reinforcement | in this case | for the most part |
| also | namely | in most cases |
| furthermore | in other words | usually |
| moreover | Result/consequence | Highlighting |
| what is more | so | in particular |
| in addition | therefore | particularly |
| besides | as a result/consequence | especially |
| above all | accordingly | mainly |
| as well (as) | consequently | Reformulation |
| in the same way | because of this/that | in other words |
| not only … but also | thus | rather |
| Similarity | hence | to put it more simply |
| equally | for this/that reason | Expressing an alternative |
| likewise | so that | alternatively |
| similarly | in that case | rather |
| correspondingly | under these circumstances | on the other hand |
| in the same way | Deduction | the alternative is |
| Transition to new point | then | another possibility would be |
| now, | in other words | Contrast |
| as far as x is concerned | in that case | instead |
| with regard/reference to | otherwise | conversely |
| as for … | this implies that … | on the contrary |
| it follows that | if so/not | in contrast |
| turning to | Stating the obvious | in comparison |
| Summary | obviously | Concession (sth unexpected) |
| in conclusion | clearly | however |
| to conclude | naturally | even though |
| in brief | of course | however much |
| to summarize | as can be expected | nevertheless |
| overall | surely | still |
| therefore | after all | yet |
Here are just a few examples of some of the words in action:
REINFORCEMENT
Desktop computers are cheaper and more reliable than laptops; furthermore, they are more flexible.
RESULT/CONSEQUENCE
Prices fell by more than 20% last year. As a result, sales increased by 15%.
GENERALISING
On the whole, his speech was well received, despite some complaints from new members.
CONTRAST
The South East of the UK often has the coldest weather in the winter. Conversely, the North West of Scotland frequently has the mildest temperatures.
CONCESSION
It was a very expensive holiday, the weather was bad and the people weren’t very friendly. Nevertheless, we would probably go back to the same place.
Get yourself or your kids enrolled in our Online Classes and experience the blended learning environment.
We provide Online tuition, homework help or assignment help. Or just simply join these classes and improve and enhance your writing skills.
Get your self registered for free and Book your Free Lesson today with one of our experts !
Click the link below to
Book Your First Online Lesson for free !